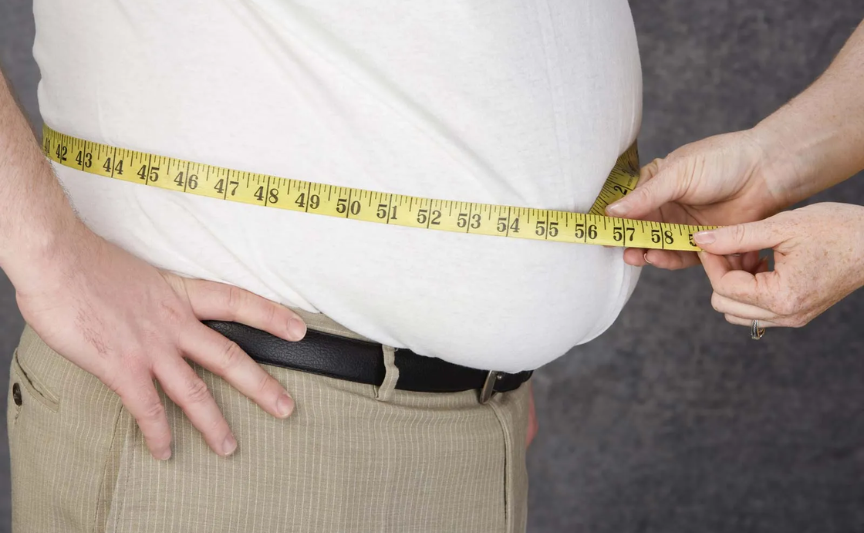

Obesity
Obesity:
Obesity is a complex, chronic condition characterized by excessive accumulation of body fat. It is a major public health concern worldwide, with significant implications for both individual health and healthcare systems.
Type of Obesity:
- Obesity can be classified based on body mass index (BMI), waist circumference, and other measures of body composition.
- It can result from a combination of genetic, environmental, socioeconomic, and behavioral factors.
Effects:
- Obesity is associated with an increased risk of numerous health problems, including type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, hypertension, stroke, certain cancers, and musculoskeletal disorders.
- It can also lead to psychological issues such as depression, low self-esteem, and social stigmatization.
Precautions:
- Adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and sufficient sleep.
- Seeking support from healthcare professionals, including dietitians, psychologists, and exercise physiologists, for personalized treatment plans.
- Avoiding crash diets or extreme weight loss measures that can be harmful in the long term.
- Addressing underlying factors contributing to obesity, such as hormonal imbalances, medication side effects, or emotional eating patterns.
Benefits:
- Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight can improve overall health and reduce the risk of obesity-related complications.
- Lifestyle modifications aimed at weight loss can lead to improvements in blood pressure, cholesterol levels, blood sugar control, and overall quality of life.
- Enhanced mobility, self-esteem, and social well-being are additional benefits of successful weight management.
